This blog explores the BTech Cyber Security course structure, top colleges in India, admission process, syllabus, placements, and career scope—with a focus on its growing importance in ethical hacking and cyber forensics.
What is BTech in Cyber Security?
BTech in Cyber Security is a 4-year undergraduate engineering program designed to equip students with the technical expertise needed to secure digital systems, networks, and data from cyber threats. It blends the principles of Computer Science, Information Technology, and Security Engineering to create professionals capable of preventing, detecting, and responding to cyberattacks.
The course dives deep into subjects like network security, cryptography, data privacy, digital forensics, and ethical hacking, giving students both theoretical understanding and hands-on experience. Unlike a generic computer science degree, BTech Cyber Security focuses specifically on safeguarding digital environments—making graduates highly specialised and in-demand in today’s data-driven world.
Students learn to work with real-world cybersecurity tools, penetration testing kits, and forensic investigation software. The curriculum often includes AI-integrated security, cloud protection mechanisms, and blockchain-based data integrity systems, aligning education with emerging technologies shaping 2026 and beyond.
By the end of the program, graduates can analyse vulnerabilities in systems, design secure networks, trace cybercrimes, and enforce information security policies. They become adept at balancing technology and ethics—understanding not only how to hack, but how to defend responsibly.
This course is ideal for students passionate about ethical hacking, digital forensics, data privacy, and national security, and who want to build careers in fast-growing roles such as Cyber Security Analyst, Security Engineer, Pen Tester, or Forensic Expert.
BTech Cyber Security Eligibility Criteria
To pursue a BTech in Cyber Security, candidates must meet a few academic and entrance-based requirements set by universities and technical institutions across India. Since this program falls under the engineering stream, eligibility largely aligns with other BTech specialisations — but with a focus on students having strong foundations in Mathematics, Physics, and Computer Science.
| BTech Cyber Security Eligibility Criteria | Details |
| Educational Qualification | Must have completed 10+2 (Class 12) or equivalent from a recognised board. Core subjects: Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics (PCM); Computer Science is an added advantage.• Minimum marks: 50%–60% aggregate in PCM (5% relaxation for SC/ST/OBC candidates). |
| Entrance Exams for Admission | Admission is primarily based on engineering entrance exams.• National Level: JEE Main, JEE Advanced (for IITs, NITs, IIITs).• State Level: MHT CET, KCET, WBJEE, AP EAMCET, TS EAMCET.• University Level: VITEEE (VIT), SRMJEEE (SRM), AEEE (Amrita), CUET-UG, BITSAT, etc. Some colleges also offer direct admission based on Class 12 merit. |
| Age Limit | Candidates must be at least 17 years old at the time of admission.• Upper age limit (if applicable) varies by exam — e.g., JEE Main: 24 years for the General category (relaxations for reserved categories). |
BTech Cyber Security Admission
Admission to a BTech in Cyber Security program in India is based on a combination of entrance exam performance, academic merit, and counselling rounds conducted by universities or government authorities. With cyber security becoming one of the fastest-growing BTech specialisations, more institutions are introducing specialised seats for this program in 2026.
Let’s break down the admission process step by step:
Entrance-Based Admission
Most reputed colleges — including IITs, NITs, IIITs, and top private universities — admit students through engineering entrance exams.
- Candidates must appear for JEE Main or a state-level entrance test such as MHT CET, KCET, WBJEE, or AP EAMCET.
- Based on scores, students participate in centralised counselling rounds (JoSAA, CSAB, or state-level) where seats in Cyber Security branches are allotted.
- Private universities like VIT, SRM, and Amrita University conduct their own entrance exams — VITEEE, SRMJEEE, and AEEE, respectively.
BTech Cyber Security Direct Admission (Merit or Management Quota)
For colleges that don’t require an entrance test:
- Admission is based on Class 12 marks (PCM aggregate) and availability of seats.
- Some universities offer management quota or institutional-level counselling for direct entry.
- Students applying through this route often need to pay a slightly higher fee, depending on the institution.
BTech Cyber Security Lateral Entry (For Diploma Holders)
- Candidates with a 3-year Diploma in Computer Science, IT, or related disciplines can directly join the 2nd year of BTech Cyber Security.
- Admission is merit-based or through specific lateral entry exams like LEET or state polytechnic entrance tests.
Counselling and Seat Allotment
- After qualifying exams, candidates must register for centralised or university-level counselling sessions.
- Seats are allotted based on entrance exam rank, college preference, and category.
- Once allotted, students confirm admission by paying the first-year fee and submitting documents like mark sheets, admit cards, and ID proofs.
BTech Cyber Security Admission Process 2026
| Admission Type | Exam / Basis | Institutions Covered | Admission Timeline (Tentative) |
| National Level Entrance | JEE Main / JEE Advanced | IITs, NITs, IIITs | Jan–May 2026 |
| State Level Entrance | MHT CET, KCET, WBJEE, AP EAMCET, etc. | State Govt. Colleges | Apr–Jul 2026 |
| University Level Entrance | VITEEE, SRMJEEE, AEEE, CUET-UG | Private & Deemed Universities | Mar–Jun 2026 |
| Direct Admission (Merit / Management) | Class 12 Marks (PCM) | Private Colleges | May–Aug 2026 |
| Lateral Entry (Diploma Holders) | LEET / State Polytechnic Exams | Govt. & Private Colleges | Jun–Aug 2026 |
Btech Cyber Security or BSc Cyber Security Which is Better?
Both BTech Cyber Security and BSc Cyber Security are excellent undergraduate programs for students who wish to build careers in information security, ethical hacking, or digital forensics. However, they differ in depth, duration, and career trajectory — and the right choice depends on your goals, aptitude, and future plans.
Let’s break down the difference clearly:
| Parameter | BTech Cyber Security | BSc Cyber Security |
| Duration | 4 Years | 3 Years |
| Type of Course | Engineering (Technical) | Science (Conceptual) |
| Eligibility | 10+2 with PCM | 10+2 with Science or Computer Science |
| Admission Process | Through Entrance Exams (JEE, CET, VITEEE, etc.) | Merit-Based or University-Level Entrance |
| Focus Area | Advanced Cyber Defence, AI, Network Security, and Engineering Applications | Cyber Laws, Threat Analysis, System Protection |
| Practical Exposure | High (Labs, Projects, Internships) | Moderate (Theory & Limited Labs) |
| Average Annual Fee | ₹1.5L – ₹3L | ₹70K – ₹1.5L |
| Job Roles | Cyber Security Engineer, Ethical Hacker, Security Architect | Security Analyst, Network Support Specialist |
| Average Salary (Freshers) | ₹6–10 LPA | ₹3–6 LPA |
| Higher Studies Options | MTech/MS, MBA Tech | MSc, PG Diplomas |
BTech Cyber Security Syllabus PDF
Students like you often search for a handy BTech Cyber Security Syllabus in PDF format. For your ease, we have provided a semester-wise BTech cyber security syllabus below.
Download BTech Cyber Security Syllabus PDF HERE.
BTech Cyber Security Syllabus
The BTech Cyber Security syllabus is designed to build a strong foundation in computer science, information security, network defence, and digital forensics, while gradually integrating AI, blockchain, and cloud-based security concepts. The program spans 8 semesters over 4 years, combining theory, practical labs, mini-projects, and internships.
BTech Cyber Security Subjects (Semester-Wise)
| Semester | BTech Cyber Security Subjects |
| Semester 1 | Fundamentals of Computer Programming, Engineering Mathematics I, Physics for Computing, Digital Logic Design, Communication Skills, Environmental Science, Programming Lab (C/Java). |
| Semester 2 | Data Structures, Engineering Mathematics II, Computer Organisation, Discrete Mathematics, Operating Systems, Database Management Systems (DBMS), DBMS Lab, Data Structures Lab. |
| Semester 3 | Computer Networks, Design & Analysis of Algorithms, Object-Oriented Programming (C++/Java), Cyber Laws & Ethics, Web Technologies, Algorithm Lab, Web Development Lab. |
| Semester 4 | Information Security Fundamentals, Cryptography & Network Security, Linux Administration, Microprocessors & Computer Architecture, Probability & Statistics, Security Lab (Linux/Network Simulation). |
| Semester 5 | Ethical Hacking, Digital Forensics, Malware Analysis, Cloud Security, Data Communication & IoT Security, Ethical Hacking Lab, Forensics Lab. |
| Semester 6 | Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Security, Blockchain Technology, Mobile & Wireless Security, Cyber Threat Intelligence, Machine Learning Basics, AI/ML Lab, Mini Project I. |
| Semester 7 | Advanced Cyber Security, Penetration Testing, Cyber Risk Management, Cybercrime Investigation, Elective I (e.g., Cyber-Physical Systems, Big Data Security), Internship/Industry Training. |
| Semester 8 | Elective II (e.g., Quantum Cryptography, Privacy & Compliance, Cloud Forensics), Elective III (AI Threat Defence, Cyber Policy), Major Project/Thesis, Seminar on Emerging Cyber Technologies. |
Core Laboratory & Practical Courses
- Programming Labs (C, Python, Java)
- Network Security Lab
- Linux & Server Configuration Lab
- Ethical Hacking & Penetration Testing Lab
- Digital Forensics & Malware Analysis Lab
- AI/ML for Security Lab
- Blockchain Implementation Lab
These labs are aimed at hands-on exposure to real-world tools like Wireshark, Kali Linux, Metasploit, Nmap, Burp Suite, Autopsy, and Snort.
Electives (Institute-Specific Options)
Students can choose electives from advanced domains based on interest or specialisation track:
- Cyber-Physical Systems Security
- Quantum Computing & Cryptography
- Cloud & Virtualisation Security
- Security in IoT and Smart Devices
- Big Data Analytics for Security
- AI in Threat Detection
- Privacy & Legal Compliance
Projects, Internships & Industry Interaction
- Mini Project I & II (Semester 6 & 7) — Industry-oriented problem-solving projects.
- Full Internship (Semester 7) — 6–8 weeks of industrial training in a cybersecurity or IT organisation.
- Major Project (Semester 8) — Research-based capstone project with real-world applications in ethical hacking, network defence, or forensic analysis.
Outcome of the BTech Cyber Security Syllabus
By the end of the program, students develop:
- Proficiency in vulnerability assessment, threat modelling, and system security design.
- The ability to use machine learning and blockchain for automated defence systems.
- Competence in forensic investigation and compliance with cyber laws.
BTech Cyber Security Colleges in India
Cybersecurity has rapidly evolved into a core focus area in Indian technical education. While IITs and NITs mostly integrate Cyber Security as a specialisation or elective track within Computer Science, Electrical, or Interdisciplinary Engineering, several private universities now offer a dedicated 4-year BTech in Cyber Security program approved by AICTE.
Below is a categorised list highlighting both government and private institutions offering strong pathways in Cyber Security education.
Government Colleges Offering Cyber Security Specialisations
In top government institutions like IITs and NITs, Cyber Security is offered as:
- A specialisation or minor within BTech in Computer Science or ECE.
- A 5-year Dual Degree (BTech + MTech) program in Computer Science with a focus on Cyber Security or Information Security.
- Some institutes also host dedicated research labs and MTech/MS programs in the same field.
BTech Cyber Security Best Colleges Government
| Institute | Program Offered | Mode of Offering | Location |
| IIT Delhi | BTech in CSE with Minor in Cyber Security / Dual Degree (BTech + MTech in CSE – Cyber Security Specialisation) | Specialisation / Dual Degree | New Delhi |
| IIT Kanpur | BTech in CSE with Cyber Security Electives / Dual Degree (BTech + MTech in Cyber Security) | Specialisation / Dual Degree | Uttar Pradesh |
| IIT Madras | BTech in CSE with Focus Area in Network & Cyber Security | Elective / Focus Track | Tamil Nadu |
| IIT Hyderabad | BTech in Artificial Intelligence / CSE with Cyber Security Modules | Specialisation / Elective | Telangana |
| IIT Bombay | BTech in CSE with Security Systems Electives | Elective Track | Maharashtra |
| IIT Kharagpur | Dual Degree (BTech + MTech in Information Security) | Dual Degree Program | West Bengal |
| NIT Tiruchirappalli | 5-year Dual Degree (BTech + MTech in CSE with Cyber Security Specialisation) | Dual Degree Program | Tamil Nadu |
| NIT Delhi | BTech in CSE with Electives in Cyber Security and Cryptography | Elective Track | New Delhi |
| NIT Patna | Integrated BTech + MTech (Cyber Security) | Dual Degree Program | Bihar |
| IIIT Allahabad | BTech in Information Technology with Cyber Security Electives | Specialization Track | Uttar Pradesh |
BTech Cyber Security Best Colleges Private
Private and deemed universities have been quicker to launch specialised 4-year BTech Cyber Security programs, focusing on practical training, ethical hacking, forensics, and AI-driven defence systems. Most of these colleges have dedicated cyber labs, industry tie-ups, and certification-based learning.
| Institute | Program Offered | Key Highlights | Location |
| Vellore Institute of Technology (VIT) | BTech in Cyber Security | AICTE-approved specialisation, top-ranked private university, and strong placements in the security domain | Tamil Nadu |
| SRM Institute of Science and Technology | BTech in Cyber Security | Global curriculum, dedicated ethical hacking lab, and international internships | Chennai, Tamil Nadu |
| Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham | BTech in Cyber Security | UGC-approved; research-driven program with blockchain and IoT integration | Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu |
| Chitkara University | BTech in Cyber Security | Industry-aligned program with Cisco and EC-Council tie-ups | Punjab |
| NorthCap University (NCU) | BTech in Cyber Security | Partnered with industry leaders for live projects and certifications | Gurugram, Haryana |
| Galgotias University | BTech in Cyber Security | AICTE-approved; practical approach with ethical hacking and forensics | Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh |
| Lovely Professional University (LPU) | BTech in Cyber Security | Offers both regular and honours degrees with optional certification programs | Jalandhar, Punjab |
| Amity University | BTech in Cyber Security | Dedicated cyber lab, dual degree and integrated options available | Noida, Uttar Pradesh |
| Jain University | BTech in Cyber Security | Strong focus on data protection and cyber intelligence | Bengaluru, Karnataka |
| REVA University | BTech in Cyber Security | Industry-integrated curriculum and project-based learning | Bengaluru, Karnataka |
| GITAM University | BTech in Cyber Security | Offers core labs for network, forensics, and malware analysis | Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh |
| Hindustan Institute of Technology & Science (HITS) | BTech in Cyber Security | Curriculum includes cloud security, digital forensics, and ethical hacking | Chennai, Tamil Nadu |
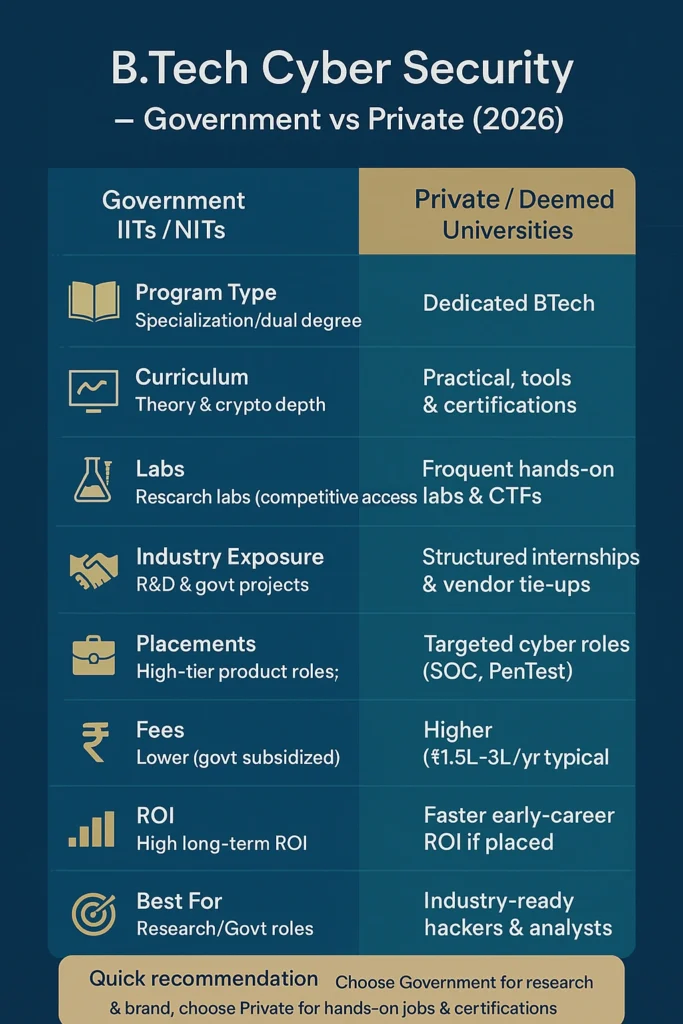
Comparative Analysis Report B.Tech Cyber Security Government (IITs/NITs/State) vs Private Colleges
-
Government (IITs / NITs / Central/State): deeper theoretical grounding, stronger research & brand value, better for R&D, public sector & top-tier roles — but cybersecurity is often delivered as a specialisation/minor/dual degree inside CSE/ECE rather than as a frequent standalone 4-yr BTech named “Cyber Security”. Dual-degree tracks (BTech+MTech) are common and powerful.
-
Private / Deemed Universities: faster to market with dedicated BTech (Cyber Security) programs, richer hands-on lab exposure, industry tie-ups, bootcamps & certifications, and pragmatic placement pipelines. Better for students who want direct, job-ready outcomes in ethical hacking, SOC roles, and product security.
Both paths lead to strong careers — choice depends on whether a student wants research/deep theory & prestige (govt) or industry-ready skills & practical exposure (private).
Download Comparative Analysis Report BTech Cyber Security Government Vs Private Colleges Here.
BTech Cyber Security Salary in India
Cyber Security has become one of the highest-paying engineering domains in India, driven by the country’s rapid digitalisation, cloud adoption, and increasing cyber threats. Graduates with a BTech in Cyber Security or a specialisation in Information Security/Ethical Hacking are in high demand across IT companies, banks, consulting firms, startups, and government agencies.
The salary after BTech Cyber Security depends on several factors — including job role, skill certifications, experience, company size, and location. Let’s break it down.
BTech Cyber Security Average Salary Overview
| Experience Level | Typical Roles | Average Annual Salary (INR) |
| Entry-Level (0–2 years) | Cyber Security Analyst, Network Security Engineer, SOC Analyst | ₹4 LPA – ₹8 LPA |
| Mid-Level (3–6 years) | Ethical Hacker, Security Consultant, Incident Response Analyst | ₹8 LPA – ₹15 LPA |
| Senior-Level (7+ years) | Cyber Security Architect, Penetration Testing Lead, Security Manager | ₹15 LPA – ₹30 LPA+ |
| Top/Executive Level | Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), Security Director | ₹35 LPA – ₹60 LPA+ |
Graduates from premier institutes like IITs, NITs, VIT, SRM, and Amrita often start on the higher end of the spectrum, especially if they hold additional certifications like CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker), CISSP, CompTIA Security+, or CHFI.
What is the salary of BTech Cyber Security?
Below is the salary of BTech cyber security with their job roles.
| Industry / Domain | Average Salary Range (INR per annum) |
| IT & Software Services (TCS, Infosys, Wipro) | ₹5 – ₹9 LPA |
| Consulting (Deloitte, PwC, EY, KPMG) | ₹8 – ₹15 LPA |
| Banking & FinTech (HDFC, Paytm, Razorpay) | ₹9 – ₹18 LPA |
| Cybersecurity Startups | ₹6 – ₹12 LPA |
| Government / Defense (DRDO, NIC, CERT-In) | ₹7 – ₹14 LPA |
| Product Companies (Google, Microsoft, Palo Alto Networks) | ₹15 – ₹35 LPA+ |
BTech Cyber Security Jobs
A BTech in Cyber Security opens the door to one of the most dynamic and in-demand career landscapes in the technology sector. With every organisation — from startups to governments — relying on digital infrastructure, cybersecurity professionals have become indispensable to protect systems, data, and networks from increasingly complex cyber threats.
In 2026, India’s cybersecurity job market is projected to exceed 1.5 million open positions, spanning diverse roles across IT, finance, defence, e-commerce, and consulting sectors. Let’s explore the key career pathways and job profiles available to BTech Cyber Security graduates.
| Job Role | Average Salary Range (INR per annum) | Description |
| Cyber Security Analyst | ₹5 – ₹8 LPA | Monitors networks, identifies threats, and ensures systems remain secure. |
| Ethical Hacker / Penetration Tester | ₹6 – ₹12 LPA | Tests system vulnerabilities and strengthens defence mechanisms. |
| Network Security Engineer | ₹5 – ₹10 LPA | Designs secure network architectures and firewalls. |
| Information Security Officer | ₹8 – ₹14 LPA | Implements and enforces security policies across an organisation. |
| Cyber Forensics Expert | ₹7 – ₹15 LPA | Investigates breaches, traces data thefts, and provides forensic reports. |
| Security Consultant (Corporate/Govt) | ₹10 – ₹18 LPA | Advises organisations on cybersecurity strategy and compliance. |
| AI Security Specialist | ₹12 – ₹20 LPA | Works on AI-driven threat detection and predictive cybersecurity systems. |
| CISO / Head of Security | ₹30 – ₹60 LPA+ | Senior leadership role responsible for enterprise-wide cybersecurity strategy. |
BTech Cyber Security Government Jobs
Cybersecurity professionals are increasingly recruited by Indian government organizations focused on national security, digital policy, and cybercrime prevention:
- DRDO (Defence Research and Development Organisation) – Cyberwarfare and cryptography units
- CERT-In (Indian Computer Emergency Response Team) – Incident response and policy roles
- National Informatics Centre (NIC) – Secure software and data centre operations
- Ministry of Home Affairs (Cyber Crime Division) – Forensic analysis and investigations
- ISRO & Armed Forces – Communication and defence system protection
Government cybersecurity positions typically offer ₹6–15 LPA along with job stability and the opportunity to work on critical infrastructure protection.
BTech in Cyber Security Online Mode
As digital education continues to evolve, many universities in India and abroad now offer BTech in Cyber Security through online, distance, or hybrid modes.
However, since BTech is an engineering degree regulated by AICTE, only a limited number of institutions are approved to offer it in fully online or hybrid mode — most follow a blended model, combining online theory classes with offline practical/lab sessions.
BTech in Cyber Security Online
An Online or Distance BTech in Cyber Security is a 4-year undergraduate program (or 3 years for lateral entry) designed to teach the same core concepts as a regular degree — including network security, ethical hacking, cryptography, and digital forensics — but delivered via virtual classrooms, e-labs, and online assessments.
BTech in Cyber Security Online Eligibility
| Criteria | Details |
| Duration | 4 Years (8 Semesters); 3 Years for Lateral Entry (Diploma Holders) |
| Eligibility | 10+2 (PCM) with 50–60% marks from a recognised board |
| Lateral Entry | 3-year Polytechnic Diploma in Computer Science / IT or Equivalent |
| Learning Mode | Fully Online / Hybrid (Online theory + Offline practicals) |
BTech in Cyber Security Online: Top Colleges
| University / Institute | Mode | Highlights |
| Amity University Online | Fully Online | UGC-entitled online BTech with electives in Cyber Security and AI; includes live projects and virtual labs. |
| IGNOU (Indira Gandhi National Open University) | Distance + Practical Workshops | Offers BTech (Information Technology & Cyber Security) through the School of Engineering and Technology with hybrid practical sessions. |
| Manipal University Jaipur (Online Manipal) | Online Mode | AICTE-approved online BTech specialisation with cybersecurity electives and internship options. |
| Lovely Professional University (LPU Online) | Hybrid Mode | Offers BTech in Computer Science (Cyber Security specialisation) with live classes and on-campus lab immersion. |
| Chandigarh University (CU Online) | Fully Online | UGC-approved; includes AI, blockchain, and forensic modules in the cybersecurity stream. |
| Vignan University (Andhra Pradesh) | Hybrid Mode | Includes weekend lab sessions for network and ethical hacking courses. |
| BITS Pilani WILP (Work Integrated Learning Program) | Online + Industry-linked | Designed for working professionals; specialisation in Information Security & Cyber Forensics. |
By 2030, India is projected to need 1.5 million+ cybersecurity professionals, with average salaries expected to grow 20–25% year-over-year. As companies adopt cloud, IoT, and AI-based systems, cybersecurity roles are expanding beyond IT departments into every major industry — from healthcare to finance and defence.
FAQs
What is BTech in Cyber Security?
BTech in Cyber Security is a 4-year undergraduate engineering program that focuses on protecting computer systems, networks, and data from cyber threats. The course covers areas like ethical hacking, cryptography, network security, digital forensics, and AI-based threat detection, preparing students for careers as cyber analysts, penetration testers, and forensics experts.
What is the eligibility for BTech Cyber Security in India?
To apply, students must have completed 10+2 (Class 12) with Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics (PCM) from a recognized board, securing at least 50–60% aggregate marks. Admission is usually through JEE Main, State CETs, CUET, or university-level entrance exams like VITEEE or SRMJEEE. Diploma holders can apply via lateral entry directly into the 2nd year.
What is the average fee for BTech in Cyber Security?
The annual fee for BTech Cyber Security ranges from ₹60,000 – ₹1,00,000 in government colleges and ₹1.5 Lakh – ₹3 Lakh in private universities like VIT, SRM, and Amity. Online or hybrid BTech programs may cost 40–50% less, depending on the mode and university.
What is the average salary after completing BTech Cyber Security?
Fresh graduates typically earn between ₹5–8 LPA, while professionals with experience or certifications like CEH, CISSP, or CHFI can earn ₹15–25 LPA or higher. Senior-level roles such as Cyber Security Architect or CISO can command salaries above ₹30 LPA, especially in consulting and tech product firms.
Which are the best colleges for BTech Cyber Security in India?
Top institutes include VIT Vellore, SRM Institute, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Chitkara University, and Amity University for specialized Cyber Security programs. Among government institutions, IIT Delhi, IIT Kanpur, NIT Trichy, and NIT Patna offer Cyber Security as a specialization or dual-degree track within Computer Science.
Can I study BTech in Cyber Security online?
Yes, select universities like Amity Online, Manipal Online, LPU Online, and Chandigarh University offer AICTE and UGC-approved online or hybrid BTech Cyber Security programs. These include live virtual classes, e-labs, and optional offline practicals. However, fully online BTech degrees are limited — always verify accreditation before enrolling.


![Bachelor of Science [B.Sc] (Agriculture) Complete Guide 2025-2026 bsc agriculture](https://articles.findmycollege.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/bsc-agriculture-170x150.jpg)
