The Diploma in Computer Science (often known as Diploma in Computer Science and Engineering or Polytechnic CSE) is a popular 3-year technical program after 10th grade, designed to build strong foundational skills in computing, programming, hardware, software, and emerging technologies. It prepares students for entry-level roles in IT, software development, web design, networking, and system support, or serves as a stepping stone to higher studies like B.Tech/BE in Computer Science.
This comprehensive guide covers everything you need: detailed course overview, semester-wise syllabus, core and elective subjects, typical course structure across 6 semesters, recommended books for key topics, and links to syllabus PDFs from various state boards and institutions (where available). Whether you’re a student planning to enroll, a parent exploring options, or someone seeking to understand the curriculum, this blog breaks down the essential information to help you make informed decisions about this career-oriented program.
Diploma in Computer Science: Course Details
The Diploma in Computer Science (commonly referred to as Diploma in Computer Science and Engineering or Polytechnic CSE) is a job-oriented technical program that equips students with practical skills in programming, software development, hardware fundamentals, networking, databases, and web technologies.
| Aspect | Details |
| Duration | 3 years (6 semesters) – Full-time program (Some states/institutes offer lateral entry after 12th/IT for 2 years) |
| Eligibility | Pass in Class 10th (SSLC/Matriculation) from a recognized board, typically with minimum 35-50% marks (varies by state/institute). Subjects like Mathematics and Science are often required. Age limit usually 15-18 years at entry (no strict upper age limit in most cases). |
| Age | Minimum age generally 15 years (as on admission date); no upper age restriction in most polytechnic admissions. |
| Average Course Fee | INR 10,000 – 1,00,000 per year (total INR 30,000 – 3,00,000 for 3 years). Government polytechnics: ₹10,000–50,000 total; Private: ₹50,000–2,00,000+ total (varies widely by state and institute). |
| Average Salary (Freshers) | INR 2.5 – 5 LPA (starting); ₹15,000–40,000 per month depending on location, skills, and company. Can rise to ₹8–12 LPA with 3–5 years of experience. |
| Common Job Roles | Junior Software Developer, Web Developer, IT Support Engineer, Computer Operator, Network Technician, Data Entry Operator, Hardware Technician, System Analyst (entry-level), Technical Support Executive. |
| Top Recruiters | TCS, Infosys, Wipro, HCL, Accenture, Cognizant, IBM, Tech Mahindra, Capgemini, Government IT departments, local software firms, startups, and hardware companies like Dell/HP service centers. |
Diploma in Computer Science Syllabus
The Diploma in Computer Science syllabus typically spans three years, divided into six semesters, focusing on building foundational to advanced skills in computing, programming, hardware, and software systems. While the exact content can vary across institutions and state boards in India, the curriculum generally includes a mix of theory, practical labs, and projects. Below, we outline the semester-wise subjects for the first two years based on standard polytechnic programs. This includes core technical subjects alongside supporting topics in mathematics, sciences, and communication.
Diploma Computer Science Syllabus 1st Year
This year covers basics in mathematics, sciences, engineering fundamentals, and introductory computing concepts to establish a strong base.
First Semester
| S. No | Subject | Credit Hrs | Sessional | Univ. Exam | Total | Periods/Week |
| Theory Courses | ||||||
| 1 | Communication Skill – I | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| 2 | Applied Maths-I | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| 3 | Electrical and Electronics Engg. | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| 4 | Elements of Mechanical Engg. | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| 5 | Fundamental of Computers | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| Practical Courses | ||||||
| 1 | Electrical and Electronics Engg. | 2 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 2 |
| 2 | Workshop Practice | 2 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 3 |
| 3 | Engineering Drawing | 2 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 3 |
| 4 | P.C.Software Lab. | 2 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 2 |
| Total | 28 | 320 | 380 | 700 | 30 | |
Second Semester
| S. No | Subject | Credit Hrs | Sessional | Univ. Exam | Total | Periods/Week |
| Theory Courses | ||||||
| 1 | Applied Maths-II | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| 2 | Applied Physics | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| 3 | Electronics Devices and Application | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| 4 | Engineering Chemistry & Environmental Science | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| 5 | Programming in C | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| Practical Courses | ||||||
| 1 | Applied Physics | 2 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 2 |
| 2 | Electronics Devices and Application | 2 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 2 |
| 3 | Engineering Chemistry | 2 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 2 |
| 4 | Programming in C | 2 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 2 |
| Total | 28 | 320 | 380 | 700 | 28 | |
Diploma Computer Science Syllabus IInd Year
The second year shifts toward core computer science topics like programming paradigms, systems architecture, and data management, with increased emphasis on hands-on labs.
Third Semester
| S. No | Subject | Credit Hrs | Sessional | Univ. Exam | Total | Periods/Week |
| Theory Courses | ||||||
| 1 | Computer-Oriented Numerical Methods | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| 2 | Object Oriented Programming | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| 3 | Signals & Systems | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| 4 | Computer Architecture | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| 5 | Digital Electronics | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| Practical Courses | ||||||
| 1 | Object Oriented Programming | 2 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 2 |
| 2 | Computer Workshop | 2 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 2 |
| 3 | Computer System & Maintenance | 2 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 2 |
| 4 | Digital Electronics Lab | 2 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 2 |
| Total | 28 | 320 | 380 | 700 | 28 | |
Fourth Semester
| S. No | Subject | Credit Hrs | Sessional | Univ. Exam | Total | Periods/Week |
| Theory Courses | ||||||
| 1 | Communication Skills – II | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| 2 | Database Management System | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| 3 | Operating System | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| 4 | Data Structures | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| 5 | Microprocessor & Microcontroller | 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 4 |
| Practical Courses | ||||||
| 1 | Database Management System | 2 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 2 |
| 2 | Operating System | 2 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 2 |
| 3 | Data Structures | 2 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 2 |
| 4 | µP Programming | 2 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 2 |
| Total | 28 | 320 | 380 | 700 | 28 | |
Diploma in Computer Science Syllabus PDF
Below is the downloadable PDF of the Diploma in Computer Science Syllabus which you can download from below:
Diploma in Computer Science Syllabus
Diploma in Computer Science Subjects
The Diploma in Computer Science curriculum encompasses a wide range of subjects that blend foundational engineering principles with core computing concepts and advanced technologies. These subjects are designed to equip students with both theoretical knowledge and practical skills essential for IT careers. Below, we’ve categorised them into foundational, core, advanced, elective, and practical/lab subjects for clarity. Descriptions are generalised based on standard polytechnic programs in India, drawing from common curricula across institutions. Each subject includes key topics typically covered.
Foundational Diploma in Computer Science Subjects
These build basic skills in mathematics, sciences, and engineering.
| Subject | Key Topics |
| Applied Mathematics-I | Algebra (progressions, binomial theorem), determinants, matrices, coordinate geometry, vectors. |
| Applied Mathematics-II | Differential calculus, integral calculus, applications of calculus (maxima/minima, tangents), differential equations, complex numbers. |
| Applied Physics | Units and dimensions, electrostatics and capacitance, electromagnetism, magnetic properties, atomic models and nuclear physics. |
| Electrical and Electronics Engineering | DC circuits, electrostatics and capacitance, electromagnetism, AC circuits, electronics components (transistors, sources). |
| Elements of Mechanical Engineering | Power transmission (belts, chains, gears), steam generators and turbines, internal combustion engines, pumps and compressors, refrigeration and air conditioning. |
| Engineering Chemistry & Environmental Science | Volumetric/gravimetric analysis, water chemistry, corrosion and lubricants, metals/alloys, polymers and waste management. |
| Communication Skills-I | Reading comprehension, grammar (tenses, vocabulary), sentence/word formation, writing (reports, CVs, applications, letters). |
| Communication Skills-II | Advanced comprehension, direct/indirect speech, writing (dialogues, paragraphs), speaking (presentations, interviews). |
Core Computer Science Subjects
These focus on fundamental computing concepts and programming.
| Subject | Key Topics |
| Fundamentals of Computers | Digital vs. analog systems, history/generations, hardware/software elements, PC types/memory, number systems, operating systems (DOS, Windows, Unix/Linux). |
| Programming in C | Computer languages, C basics (structure, data types, operators), control statements, arrays/strings/functions, pointers/structures/files. |
| Object Oriented Programming | Structured vs. OOP, classes/objects/methods, inheritance/polymorphism/overloading, scope/inline/friend functions, templates/files/graphics. |
| Computer Architecture | CPU/register organisation, arithmetic operations, memory hierarchy (main/auxiliary/cache/virtual), input-output organisation (peripherals, interrupts, DMA). |
| Data Structures | Arrays/pointers, linked lists (singly/doubly/circular), stacks/queues, complexity/sorting/searching algorithms (insertion/bubble/selection/quick/linear/binary), graphs/trees (traversals). |
| Database Management System | Database vs. file systems, ER model, relational model/SQL (queries, joins, aggregates), normalization (1NF-3NF/BCNF), functional dependencies. |
| Operating System | OS functions/evolution/structure, processes/scheduling/deadlocks, memory management (partitioning/paging/segmentation/virtual/demand paging), file systems/disk scheduling. |
| Java Programming | Java features/data types/operators, classes/objects/methods/inheritance, packages/multithreading/exceptions, applet programming/graphics. |
Advanced Diploma in Computer Science Subjects
These cover specialised topics in software and systems.
| Subject | Key Topics |
| Computer Oriented Numerical Methods | Errors/approximations, algebraic/transcendental equations (bisection/iteration/false position/Newton-Raphson), interpolation (Newton/Gauss/Lagrange), numerical integration/differentiation (Trapezoidal/Simpson), differential equations/statistical computations. |
| Signals & Systems | Signals/systems properties, modulation (amplitude/frequency/pulse), sampling/reconstruction, linear feedback systems (root locus/Nyquist). |
| Digital Electronics | Number systems/codes, logic gates/Boolean algebra/K-maps, combinational circuits (adders/subtractors/multiplexers), flip-flops/shift registers/counters, logic families/A-D/D-A converters. |
| Microprocessor & Microcontroller | Architecture/programming model/instruction set, interrupts/I/O, peripheral interfaces (PPI/DMA/interrupt controllers/timer), interfacing signals (ADC/DAC), development tools. |
| Computer Graphics | Graphics hardware/devices, line/circle algorithms (DDA/Bresenham/mid-point), transformations/clipping (Cohen-Sutherland/Sutherland-Hodgeman), 3D primitives/viewing/projections. |
| Web Technology | Web protocols/development/applications, HTML/XHTML/XML/CSS, JavaScript (objects/events/AJAX), VB Script/CGI/PERL, web servers/security (Apache/firewalls/proxy). |
| Data Communication & Computer Networks | Data transmission/encoding/media, network models (OSI/TCP/IP), LAN topologies/protocols (Ethernet/Token Ring/FDDI), routing/congestion, transport/application layers (TCP/UDP/HTTP/FTP). |
| Software Engineering | Software characteristics/processes/SDLC models (Waterfall/Prototype/Spiral), requirements elicitation/analysis/documentation, size/cost estimation/risk management, design (modularization/flow charts), testing (functional/structural/unit/integration/system). |
| Advanced RDBMS | Database models/architecture/normalization, SQL/PL-SQL (queries/actions/views/procedures/functions/triggers), server administration (indexing/security/backup/clustering), universal data access (ODBC/OLE DB/ADO.NET/JDBC). |
| Visual Programming | .NET framework/CLR/languages (VB/C#), GUI controls/properties/events, OOP in VB.NET, ASP.NET web forms/security/database connectivity, ADO vs. ADO.NET operations. |
| Information Security & Cyber Law | Information systems threats/attacks/principles, physical security/biometrics, cryptography/digital signatures/firewalls/network security (VPN/intrusion detection), security metrics/laws/IPR/ethics/cyber crimes. |
Elective Subjects
Students typically choose one in the final semester for specialisation.
| Subject | Key Topics |
| Embedded System | Embedded architectures/specialties/trends/communication interfaces, software architectures/RTOS/tasks/semaphors, design principles/real-time scheduling, development tools/debugging. |
| Artificial Intelligence | AI definitions/goals/techniques/applications, reasoning/problem solving/search algorithms/CSPs, knowledge representation (predicate logic/rules/semantic nets/frames), expert systems (acquisition/inference/DENDRAL/MYCIN), languages (LISP/PROLOG). |
| Mobile Computing | Wireless fundamentals (transmission/modulation/MAC/multiplexing), telecommunication/satellite systems (GSM/UMTS/IMT-2000/DAB/DVB), wireless LAN (IEEE 802.11/HIPERLAN/Bluetooth), mobile IP/routing/transport (TCP/WAP). |
Practical/Lab Subjects
These emphasise hands-on implementation and experimentation.
| Subject | Key Activities |
| P.C. Software Lab | MS Office (Word/Excel/PowerPoint/Access), DOS/Windows commands/explorer. |
| Programming in C Lab | Data types/operators/expressions, decision/loops/nested loops, arrays/functions/pointers/structures/files, pattern designs/recursion. |
| Applied Physics Lab | Measurements (volume/density/curvature/pendulum), resistance/EMF/refractive index/focal length experiments. |
| Electronics Devices & Application Lab | Diode/Zener/LED characteristics, rectifier ripple factors, transistor input/output characteristics. |
| Engineering Chemistry Lab | Purity/hardness/alkalinity estimations, viscosity/moisture determinations. |
| Object Oriented Programming Lab | Control statements/structures/functions/pointers, call mechanisms/classes/inline/constructors, inheritance/overloading/virtual functions/templates/exceptions. |
| Computer Workshop Lab | Display devices/printers/motherboard/hard disk/processors/RAM/BUS/NIC/MODEM studies. |
| Computer System & Maintenance Lab | BIOS/POST/errors, OS installation/partitioning/booting, troubleshooting/printer installation/uninstallation, networking/printer sharing. |
| Digital Electronics Lab | Logic gates/universal gates/adder/subtractor truth tables/circuits. |
| Database Management System Lab | ER diagrams/table creation/insertions, SELECT queries/operators/joins/sets/aggregates/arithmetic/GROUP BY, constraints/relationships/normalization. |
| Operating System Lab | OS types/evolution/DOS/Unix commands, installation, CPU scheduling/page replacement/deadlock algorithms, memory management/file allocation simulations. |
| Data Structures Lab | Array insertions/deletions/2D operations, linked list insertions/deletions, stack/queue operations, binary tree levels/graph direction, search/sort algorithms. |
| Microprocessor Programming Lab | 8/16-bit addition/subtraction/complement/decimal operations, larger/smaller number findings. |
| Computer Graphics & Multimedia Lab | Graphics functions/scenery, line/circle algorithms/clipping, 2D/3D transformations/scaling/rotation, OpenGL scenes/multimedia films. |
| Web Technology Lab | HTML tags/pages/forms, CSS linking/frames, JavaScript validation/sorting, PHP form handling/validation. |
| Computer Networks Lab | Transmission media/cable connections, NIC/repeater/hub/bridge/switch/router studies, printer installation/configuration, IPv4 addressing. |
| Java Programming Lab | JDK setup/swapping/prime/Fibonacci/type casting, number reversal/pyramids, packages/inheritance/interfaces/exceptions/multithreading. |
| RDBMS Lab | ER diagrams (university/bank), SQL queries, PL-SQL procedures/functions/triggers, JDBC operations. |
| Visual Programming Lab | Visual Studio .NET/C# swapping/employee details/quadratic roots/pyramids/sorting/lists/searching/forms/validations, VB calculator/scientific calculator, ASP.NET master pages/resume/database connectivity/forms. |
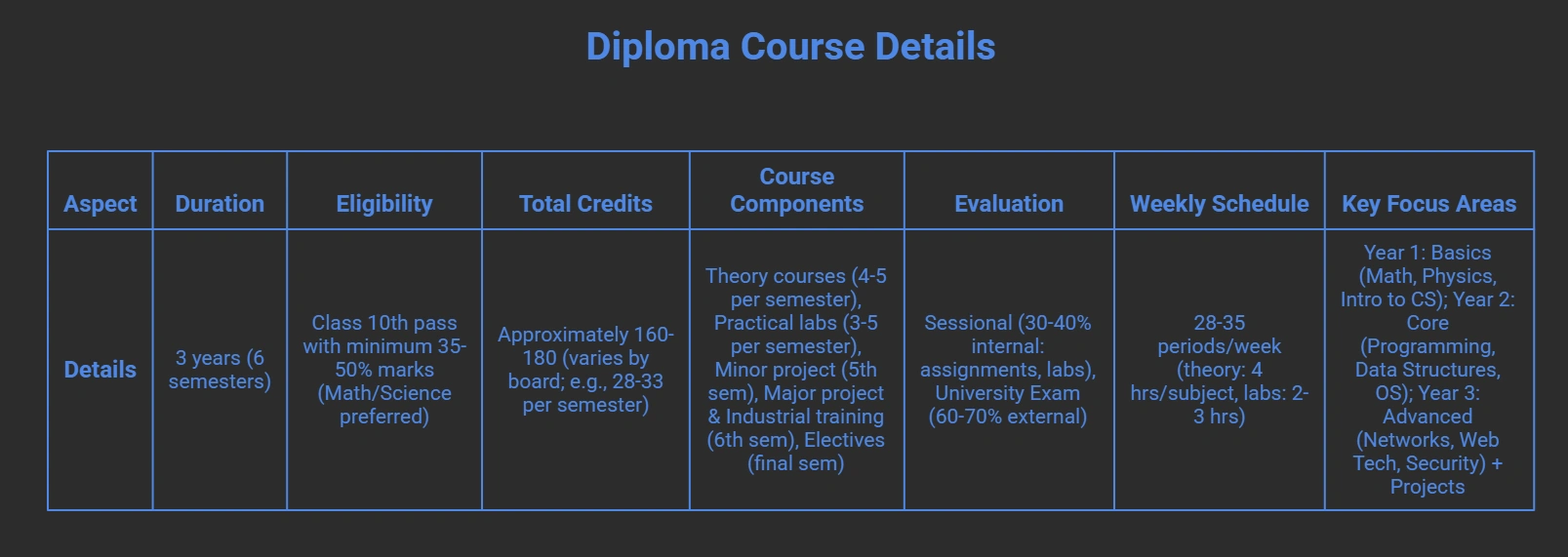
Diploma in Computer Science Course Structure
The Diploma in Computer Science (often called Diploma in Computer Science and Engineering) is a structured 3-year polytechnic program in India, divided into 6 semesters, aimed at providing practical and theoretical knowledge in computing fundamentals, programming, hardware, software development, and emerging technologies. It typically follows a credit-based system, with a mix of core theory subjects, practical labs, minor/major projects, and industrial training in the final year.
Evaluation combines internal assessments (sessional marks for assignments, labs, and attendance) and external university exams. The structure may vary slightly by state boards (e.g., BTEUP, MSBTE) or institutions, but it emphasises hands-on skills for immediate employability or further studies.
Diploma in Computer Science Subjects Books
Recommended books for the Diploma in Computer Science (or Computer Engineering) program help students grasp key concepts through clear explanations, examples, and solved problems tailored to polytechnic syllabi. Below is a consolidated table of popular and widely used reference books, trimmed to 1-2 essential recommendations per major subject.
These are student-friendly, affordable options often suggested for diploma-level studies. Prioritize books with solved examples and practice questions. Many are available as low-cost editions or PDFs from publishers like Nirali Prakashan, TechKnowledge, or Khanna Publishers.
| Subject | Recommended Books (1-2 per subject) |
| Applied Mathematics (I & II) | 1. Applied Mathematics Vol I & II by Dr. Hari Arora & A. Sachdev
2. Engineering Mathematics by B.S. Grewal |
| Applied Physics / Electronics | 1. Engineering Physics by R.K. Gaur & S.L. Gupta
2. Basic Electronics by V.K. Mehta |
| Electrical & Electronics Engineering | 1. Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering by V.K. Mehta
2. Electrical Technology by B.L. Theraja |
| Elements of Mechanical Engineering | 1. Basic Mechanical Engineering by Pravin Kumar
2. Elements of Mechanical Engineering by R.K. Rajput |
| Engineering Chemistry & Environmental Science | 1. Engineering Chemistry by P.C. Jain & M. Jain
2. A Textbook of Engineering Chemistry by S.S. Dara |
| Communication Skills (I & II) | 1. Technical Communication by Meenakshi Raman & Sangeeta Sharma
2. Communication Skills by Sanjay Kumar & Pushp Lata |
| Fundamentals of Computers | 1. Computer Fundamentals by P.K. Sinha
2. Fundamentals of Computers by V. Rajaraman |
| Programming in C | 1. Let Us C by Yashavant Kanetkar
2. Programming in ANSI C by E. Balagurusamy |
| Object Oriented Programming | 1. Object-Oriented Programming with C++ by E. Balagurusamy
2. Programming with Java: A Primer by E. Balagurusamy |
| Data Structures | 1. Data Structures Using C by E. Balagurusamy
2. Fundamentals of Data Structures in C by Ellis Horowitz, Sartaj Sahni & Susan Anderson-Freed |
| Database Management System (DBMS / Advanced RDBMS) | 1. Fundamentals of Database Systems by Ramez Elmasri & Shamkant B. Navathe
2. Database Management Systems by Raghu Ramakrishnan & Johannes Gehrke |
| Operating System | 1. Operating System Concepts by Abraham Silberschatz, Peter B. Galvin & Greg Gagne
2. Modern Operating Systems by Andrew S. Tanenbaum |
| Computer Architecture | 1. Computer System Architecture by M. Morris Mano
2. Computer Organization and Architecture by William Stallings |
| Java Programming | 1. Java: The Complete Reference by Herbert Schildt
2. Programming with Java by E. Balagurusamy |
| Web Technology / Computer Networks | 1. Data Communications and Networking by Behrouz A. Forouzan
2. Computer Networks by Andrew S. Tanenbaum |
| Software Engineering | 1. Software Engineering: A Practitioner’s Approach by Roger S. Pressman |
| Digital Electronics / Microprocessor | 1. Digital Design by M. Morris Mano
2. Microprocessor Architecture, Programming, and Applications with the 8085 by Ramesh Gaonkar |
| Computer Graphics | 1. Computer Graphics by Donald Hearn & M. Pauline Baker |
| Information Security & Cyber Law | 1. Cyber Laws and IT Protection by Harish Chander |
These selections focus on core subjects from the typical 6-semester syllabus, emphasizing practical and exam-oriented books popular in Indian diploma programs. For electives (e.g., Embedded Systems, AI, Mobile Computing), refer to specialized texts like Embedded Systems by Raj Kamal or Artificial Intelligence by Elaine Rich & Kevin Knight.
FAQs
1. What is the duration of the Diploma in Computer Science course?
The Diploma in Computer Science is a 3-year full-time program divided into 6 semesters. It starts after Class 10th and includes theory, practicals, projects, and industrial training in the final year. Some institutes offer lateral entry for 2 years after 12th. (48 words)
2. What is the eligibility criteria for admission?
Candidates must have passed Class 10th (SSLC/Matric) from a recognized board, usually with at least 35-50% marks in aggregate, including Mathematics and Science. Minimum age is typically 15 years. Admission is often merit-based or through entrance exams like polytechnic CET. (52 words)
3. What are the main subjects in the first year?
The first year (Semesters 1 & 2) focuses on foundational subjects: Communication Skills, Applied Mathematics-I & II, Applied Physics, Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Elements of Mechanical Engineering, Fundamentals of Computers, Programming in C, Engineering Chemistry, and related practical labs. (49 words)
4. What core subjects are covered in the second and third years?
Second year includes Object Oriented Programming, Data Structures, Database Management System, Operating System, Computer Architecture, Digital Electronics, and Microprocessor. Third year advances to Web Technology, Computer Networks, Java Programming, Software Engineering, Computer Graphics, and electives like AI or Embedded Systems. (50 words)
5. Are there projects and industrial training in the course?
Yes, a Minor Project is in the 5th semester, and a Major Project (with high credits) plus Industrial Training & Visits are in the 6th semester. Project topics are assigned early in the 5th semester to allow preparation and real-world application. (48 words)
6. What job roles can I get after completing this diploma?
Freshers can work as Junior Software Developer, Web Developer, IT Support Engineer, Network Technician, Hardware Technician, Database Operator, or Technical Support Executive. With experience, roles expand to System Analyst or higher positions in IT firms. (47 words)
7. What is the average starting salary after this diploma?
Starting salary for freshers ranges from ₹2.5 to 5 LPA (₹15,000–40,000 per month), depending on location, skills, and company. In metros or with certifications (e.g., Java, networking), it can be higher; experienced professionals earn ₹8–12 LPA or more. (52 words)
8. Can I pursue higher studies after this diploma?
Yes, you can join B.Tech/BE in Computer Science or related fields via lateral entry (direct 2nd year admission). Options also include BCA, advanced certifications in AI, cybersecurity, or web development to enhance career prospects.











