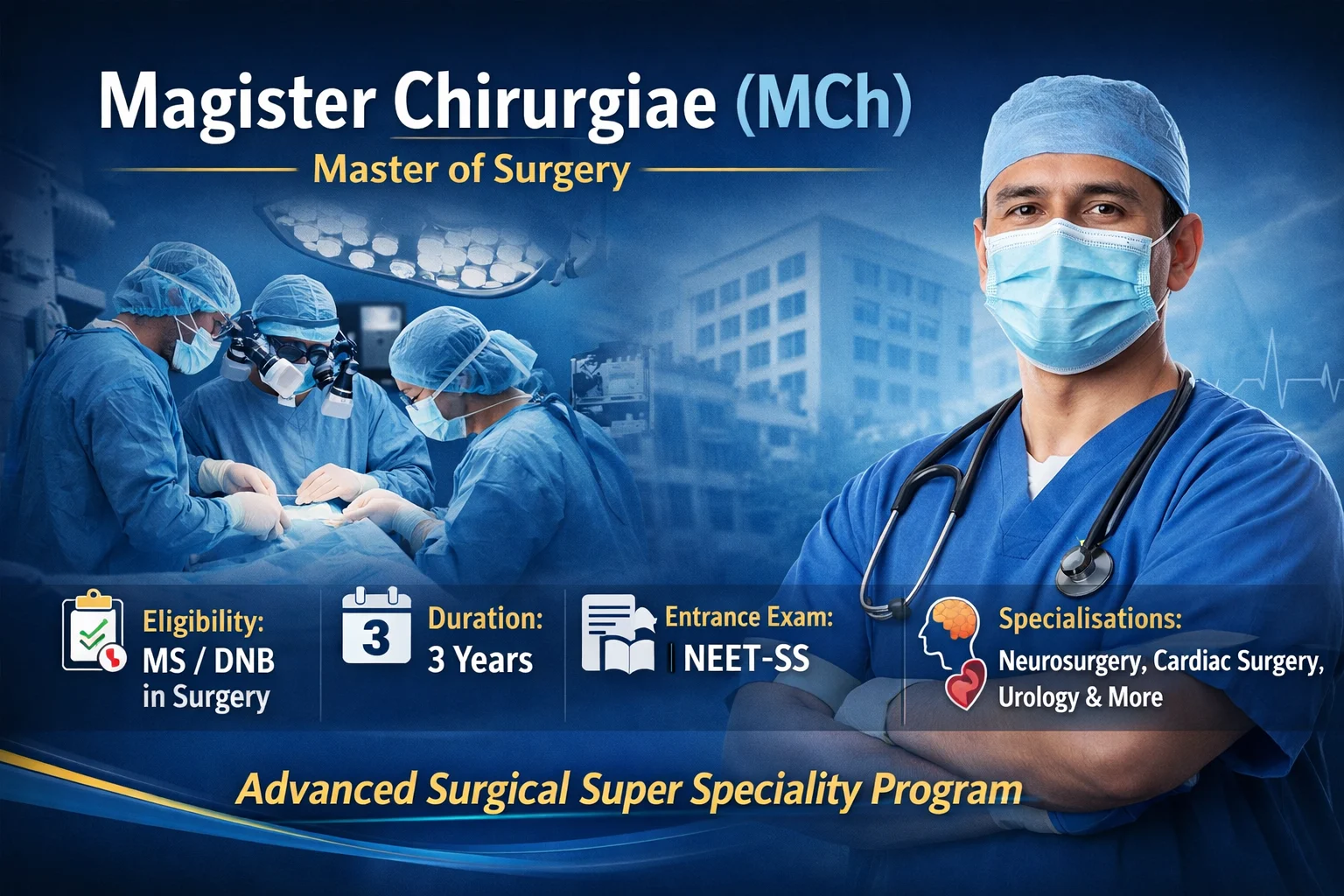
The Magister Chirurgiae (MCh) is among the most prestigious qualifications in Indian medical education and represents the highest level of super-speciality surgical training. Designed for qualified surgeons who have already completed an MS (Master of Surgery) or an equivalent postgraduate degree, the MCh programme focuses on advanced expertise in highly specialised surgical fields such as neurosurgery, cardiothoracic and vascular surgery, urology, paediatric surgery, surgical oncology, plastic and reconstructive surgery, and surgical gastroenterology.
The course emphasises intensive clinical exposure, advanced operative techniques, research involvement, and multidisciplinary management of complex surgical conditions. Admission is regulated through the NEET-SS examination, conducted by the National Board of Examinations in Medical Sciences (NBEMS), and the programme operates under the guidelines of the National Medical Commission (NMC).
Typically spanning three years, the MCh curriculum combines hands-on training in tertiary care hospitals with academic learning, seminars, thesis work, and supervised high-risk procedures. Graduates emerge as highly skilled super-specialists prepared for leadership roles in advanced clinical practice, teaching, and surgical research across India.
What Is an MCh Degree?
MCh degree full form is Magister Chirurgiae, also known as Master of Chirurgiae, a Latin term that translates to Master of Surgery. It is recognised as a super-speciality, post-doctoral surgical degree focused on advanced surgical training, specialised clinical exposure, and research methodology.
The MCh degree is pursued after completing a primary postgraduate surgical qualification such as MS (Master of Surgery) or an equivalent DNB degree. It is specifically designed for doctors who already hold an MBBS and MS/DNB in general surgery or related surgical disciplines and wish to gain mastery in highly complex surgical procedures, advanced operative techniques, and specialised patient care.
Unlike the MS degree, which provides broad training in surgical principles, the MCh programme emphasises super-specialised clinical practice, in-depth research exposure, and leadership in surgical medicine. Graduates are trained to handle intricate surgical cases, contribute to academic research, and play key roles in tertiary and quaternary healthcare settings.
Eligibility Criteria for MCh Admission
To pursue a Magister Chirurgiae (MCh) programme in India, candidates must meet strict academic and regulatory requirements, as the course is meant for advanced surgical specialisation.
Basic Eligibility Requirements
Candidates applying for an MCh course must fulfil the following criteria:
-
Completion of MS (Master of Surgery), DNB (Surgery), or an equivalent postgraduate surgical qualification from a recognised medical university or institute
-
In certain specialities, candidates with MD degrees involving surgical training may also be eligible, subject to NMC norms
-
Mandatory registration with the National Medical Commission (NMC) or the relevant State Medical Council
-
Fulfilment of speciality-specific eligibility, as MCh admissions are offered only in corresponding surgical branches (e.g., MS General Surgery for MCh Neurosurgery, Urology, etc.)
Eligibility for International Candidates
-
Medical degrees obtained abroad must be recognised by the National Medical Commission (NMC) or equivalent medical authorities
-
Candidates may be required to clear additional eligibility or screening requirements as specified by the admitting institution
In addition to academic qualifications, clinical competence, surgical aptitude, prior training exposure, and academic record play an important role during shortlisting and counselling.
MCh Admission Process & Entrance Exams
Admission to the MCh degree in India is highly competitive and follows a structured, centralised process regulated by national medical authorities.
National-Level Entrance Exam
The primary entrance examination for MCh admission is:
-
NEET-SS (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test – Super Speciality)
Conducted annually by the National Board of Examinations in Medical Sciences (NBEMS), NEET-SS is mandatory for admission to most government, private, and deemed medical colleges offering MCh courses in India.
The exam assesses:
-
Advanced clinical knowledge
-
Speciality-specific surgical understanding
-
Problem-solving and decision-making skills relevant to super-speciality practice
Institute-Level Entrance Exams
Some premier institutions conduct separate entrance examinations for MCh admission, including:
-
INI-CET for institutes under the Institutes of National Importance (INI) such as AIIMS, JIPMER, PGIMER, and NIMHANS
-
Institute-specific selection tests, interviews, or assessments conducted by select universities and autonomous medical institutions
Candidates qualifying these exams are shortlisted based on merit for further admission procedures.
Counselling & Seat Allotment
-
After qualifying NEET-SS or INI-CET, candidates participate in centralised counselling
-
Counselling is coordinated by bodies such as the Directorate General of Health Services (DGHS) or respective state authorities
-
Seat allotment is done based on:
-
Entrance exam rank
-
Speciality preference
-
Institutional availability
-
Reservation norms
-
Final admission is confirmed after document verification, eligibility clearance, and fee payment at the allotted medical college.
Magister Chirurgiae (MCh) Specialisations
MCh (Magister Chirurgiae) programmes offer focused training across numerous surgical sub‑disciplines. Each specialisation emphasises complex operative skills, multidisciplinary patient care, research ability, and high precision surgical intervention.
| Specialisation | Focus Area |
|---|---|
| Neurosurgery | Surgical care of the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves |
| Cardiothoracic Surgery (CTVS) | Heart, lung and major thoracic organ surgery |
| Paediatric Surgery | Surgical treatment for infants, children & adolescents |
| Urology | Surgical care of the urinary system and male reproductive organs |
| Surgical Oncology | Cancer surgery and tumour management |
| Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery | Cosmetic and reconstructive procedures |
| Vascular Surgery | Surgery on blood vessels and circulatory systems |
| Hepato‑Pancreato‑Biliary Surgery | Complex liver, pancreas and biliary system surgery |
| Surgical Gastroenterology | Advanced surgery of the digestive tract |
MCh Fees in India
The MCh fees vary substantially based on whether the programme is offered at a government medical college, an autonomous or deemed university, or a private medical institution. Government institutions generally subsidise tuition, while private colleges can be significantly costlier.
Typical Fee Ranges by College Type
| College Type | Approx. Fee (Annual) |
|---|---|
| Government Medical Colleges | ₹20,000 – ₹6,00,000 |
| Private/Demed Institutions | ₹1,10,000 – ₹29,00,000+ |
Here are few colleges and their fees:
| College / Institute | Type | Approx. Annual Fees (₹) | Special Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| AIIMS, New Delhi | Government | 2,200 – 15,000 | As per INI fee norms |
| PGIMER, Chandigarh | Government | Nominal range (govt) | Typical for government super-speciality courses |
| CMC, Vellore | Private / Deemed | 2,00,000+ | MCh Neurosurgery & similar programmes |
| NIMHANS, Bengaluru | Government | 1,80,000 | MCh Neurosurgery |
| Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Coimbatore | Private | 13,00,000+ | MCh Neurosurgery |
| Kasturba Medical College, Manipal | Private | 20,00,000+ | Fees vary by speciality |
| Vydehi Institute of Medical Sciences, Bengaluru | Private | 75,00,000 | Surgical Oncology (reported in media) |
| Kidwai Memorial Institute of Oncology, Bengaluru | Government | 2,40,000 | MCh Surgical Oncology, first-year fees |
(Fees below are approximate and may vary by specialisation and session)
Top MCh Colleges in India
India boasts some of the leading medical institutes globally for advanced surgical education. These colleges are recognised for their clinical excellence, research culture, high surgical case loads, and expert faculties:
Premier Government & Public Institutes
-
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi: Known for super‑speciality training across multiple MCh branches.
-
Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education & Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh: Renowned for research and specialist surgical exposure.
-
Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education & Research (JIPMER), Puducherry: Offers a range of MCh programmes with strong clinical training.
-
Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences (SGPGIMS), Lucknow: Well‑established surgical super‑speciality centre.
-
National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS), Bengaluru: Leading for Neurosurgery super‑speciality.
-
Banaras Hindu University (IMS), Varanasi: Government institute offering MCh courses.
Notable Private/Deemed Institutions
-
Christian Medical College (CMC), Vellore: High clinical exposure and strong postgraduate culture.
-
Kasturba Medical College (KMC), Manipal: Offers several MCh specialities with robust training.
-
Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Coimbatore: Prominent private option for advanced surgical degrees.
-
Vydehi Institute of Medical Sciences, Bengaluru: Expensive but well‑equipped surgical training facilities.
-
Mahatma Gandhi Medical College & Hospital, Jaipur: Offers MCh in specialised areas like Urology and Hepato‑Pancreato‑Biliary surgery with structured fee plans.
Career Scope After MCh
Completing a Magister Chirurgiae (MCh) degree significantly elevates a surgeon’s professional standing, opening access to leadership roles in advanced surgical care, academics, and research. As a recognised super-speciality qualification, the MCh degree is highly valued across India and internationally, particularly in tertiary care hospitals and advanced surgical centres.
Key Career Paths After MCh
-
Super-Specialist Surgeon / Consultant
Lead complex procedures in super-speciality hospitals, trauma centres, and advanced surgical units. -
Senior Resident / Fellow
Work in high-volume tertiary care hospitals to gain further sub-specialised exposure and operative independence. -
Academic Faculty / Professor of Surgery
Teaching roles in medical colleges and universities, combining patient care, training, and academic research. -
Clinical Researcher / Scientist
Engage in surgical trials, outcomes research, innovation in techniques, and medical technology development. -
Healthcare Administrator / Department Head
Leadership positions managing surgical departments, hospital operations, and multidisciplinary teams. -
Private Super-Speciality Practice
Establish or join high-end private surgical practices or corporate hospital networks.
Salary Prospects After MCh (India)
| Career Stage | Approx. Annual Salary |
|---|---|
| Entry Level | ₹10–20 LPA |
| Mid Career | ₹25–50 LPA |
| Senior Level | ₹50 LPA+ |
Highly experienced MCh surgeons, especially in fields like neurosurgery, surgical oncology, and cardiothoracic surgery, can earn substantially higher through private practice, international fellowships, or overseas employment in countries with advanced healthcare systems.
MCh vs MS: Key Differences Explained
| Feature | MS (Master of Surgery) | MCh (Magister Chirurgiae) |
|---|---|---|
| Level | Postgraduate surgical degree | Super-speciality / post-doctoral surgical degree |
| Duration | 3 years | 3 years |
| Eligibility | MBBS + entrance exam (NEET-PG) | MS/MD/DNB + NEET-SS or INI-CET |
| Focus Area | Broad-based training in general surgery | Highly specialised, advanced surgical training |
| Scope of Practice | General and basic specialised surgical procedures | Complex, high-risk and super-speciality surgeries |
| Clinical Exposure | Foundational operative and patient care skills | Intensive hands-on training in tertiary care settings |
| Career Outcome | General surgeon or junior specialist roles | Super-specialist surgeon, consultant, academic leader |
In essence, MS builds the foundation of surgical practice, while MCh represents advanced mastery in a specific surgical domain. An MCh degree is typically pursued by surgeons aiming for senior consultant roles, academic leadership, or highly specialised private and institutional practice.
FAQs
Q1. What is the full form of MCh?
MCh stands for Magister Chirurgiae, meaning Master of Surgery — a super-speciality surgical degree.
Q2. What is an MCh degree?
It is an advanced, super-speciality postgraduate programme for surgeons who have completed their MS or equivalent surgical qualification.
Q3. What is the duration of the MCh course?
The standard duration is 3 years of structured clinical and operative training.
Q4. Who is eligible for MCh admission in India?
Candidates must hold an MS/MD/DNB in a relevant surgical discipline and be registered with NMC or equivalent.
Q5. Which entrance exam is required for MCh?
The main exam is NEET-SS, although INI-CET and some institute-specific tests are also used.
Q6. What is the average fee for MCh in India?
Fees vary widely — from around ₹20,000 in government colleges to over ₹29,00,000 per year in private institutions.
Q7. What are popular MCh specialisations?
Neurosurgery, Cardiothoracic Surgery, Paediatric Surgery, Urology, Surgical Oncology, Plastic Surgery and Vascular Surgery are common options.
Q8. What career prospects are available after MCh?
MCh graduates can work as super-specialist surgeons, consultants, professors, research leads, and surgical administrators in top hospitals.